Blog Archives
Film Revision: Key Words
Key words
- Close-up: Used to film just the head or face.
- Cut: An instant change from one frame to another.
- Deep focus: Foreground, middle ground and background are all in focus.
- Dissolve: A move between two shots (i.e. a transition) during which the first image gradually disappears while the second image gradually appears
Example of a dissolve from Citizen Kane.
- Extreme close-up: Used to film very small details closely.
- Fade-in: Necessary for the beginning of a scene. A dark screen gradually brightens as the shot appears.
- Fade-out: A shot gradually darkens as the screen goes black.
- Fourth wall: Audience occupies the fourth wall, looking in on what is happening (as in a theatre). Breaking the fourth wall happens when a character addresses the audience, turns to the camera, comments on the fact they are aware that they are in a play etc.
Example of breaking the fourth wall from Miranda.
Example of breaking the fourth wall from Whatever Works.
- Frame: Single image.
- Long Shot: Framing in which the scale of the object shown is small.
- Melodrama: Music swells and carries emotion.
- Mise en scène: Everything on camera (costumes, lighting, colour, location, situation of objects and characters, etc.).
- Montage: Sequence of images or scenes used to compress the passage of time, suggest memories, summarise a topic, etc.
Example of a montage from Up.
- Pathetic Fallacy: Attributing human emotions to inanimate objects, animals, or aspects within nature. In other words, the atmosphere/setting echoes the mood/thoughts/emotions/conduct of the protagonist. It is an external expression of internal states and the inner protagonist becomes connected with the environment/outside world. In other words, it establishes metaphorical links between objects of abstracts. (Basic examples include rain when a character is upset or a beautiful landscape during a happy moment.)
Example of pathetic fallacy from Snow White. Note the difference in weather when the disguised Queen arrives and when she leaves.
- Point of view: There are a few variations of POV shots. Typically, it’s a shot taken where the camera is placed where the character’s eyes would be, showing what the character would see (i.e. the character is in possession of the perspective and we are looking through their eyes).
Example of a POV shot from Vertigo.
- Wipe: Type of transition in which the screen ‘wipes’ from one frame/scene to another, creating an overlap – as one scene disappears, another replaces it.
Examples of wipes, used in Star Wars III: Revenge of the Sith.
Shots
Panning: Camera swivels on its axis.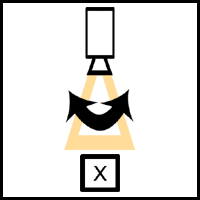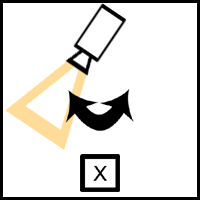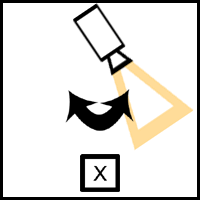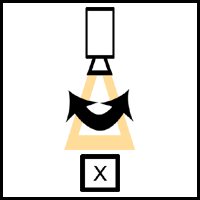
Tracking/Trucking: Mounted camera moves following the action.
Example of tracking from The Shining.
Trunk Shot: Specialised low-shot angle which captures the scene above from inside a trunk.
Example of trunk shot in Kill Bill: Vol. 1. Warning: contains blood!

























You must be logged in to post a comment.